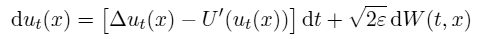
Introduction
Metastability in parabolic SPDEs
Existence of solutions for FitzHugh-Nagumo SPDEs with space-time white noise in dimensions 2 and 3
Renormalisation of space-fractional SPDEs
Metastability in parabolic SPDEs
With Barbara Gentz, I have proved an analogue of Kramers' law for parabolic stochastic partial differential equations (SPDEs) of Allen-Cahn type, of the form
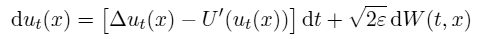
where U is a bistable potential and W(t,x) denotes space-time white noise. Detailed results are contained in this paper, and formal computations can be found here.
With Giacomo Di Gesù and Hendrik Weber, I have extended this result to Allen-Cahn equations on the 2-dimensional torus (when the torus is small enough for the identically zero solution to be the transition state). A renormalisation procedure is required for the equation and the Eyring-Kramers prefactor to be well-defined. The results are contained in this paper.
Simulation of a 2D stochastic Allen-Cahn equation with conserved magnetisation:
Existence of solutions for FitzHugh-Nagumo SPDEs with space-time white noise in dimensions 2 and 3
With Christian Kuehn, I have proved local existence and uniqueness of solutions for FitzHugh-Nagumo SPDEs of the form
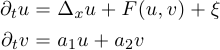
where ξ denotes space-time white noise, F is a cubic polynomial, and x is two- or three-dimensional. The proof relies on Martin Hairer's theory of regularity structures. In fact, one has to renormalise the equation to obtain a well-defined solution. This is done by regularising the noise term, convoluting it with a mollifyer supported in a ball of radius ε, and adding a term C(ε)u to the equation, where C(ε) diverges as ε goes to zero (logarithmically in dimension 2, and like 1/ε in dimension 3). In the case of a general cubic nonlinearity, the representation of the solution at the level of the regularity structure is given symbolically by

The results are contained in this paper, and a corrigendum is here.
Simulation of a 2D stochastic FitzHugh-Nagumo SPDE:
Renormalisation of space-fractional SPDEs
With Christian Kuehn, I have studied reaction-diffusion equations with fractional Laplacian of the form
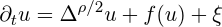
on the torus of dimension d, where f is a nonlinearity of degree N. This model is locally subcritical when ρ > ρc = d(N-1)/(N+1). In this article, we study a model space of this equation. In particular, we show that the size of the model space grows exponentially in 1/(ρ - ρc) when the subcriticality boundary is approached. The number of negative homogeneities grows like 1/(ρ - ρc). The proof is based on graphical contructions allowing to count the trees representing elements of the model space.
In this follow-up work with Yvain Bruned, we analyse the asymptotics of renormalisation counterterms as ρ decreases to ρc in the case of a quadratic nonlinearity (N = 2). We find that these counterterms behave either as a negative power of the mollification parameter ε, or as log(1/ε) depending on the values of ε and ρ - ρc.
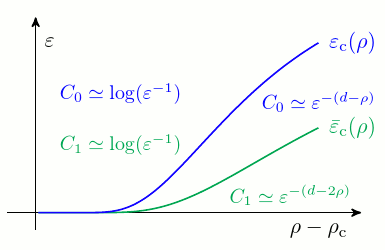
The proof is based on recent results by Yvain Bruned, Ajay Chandra, Ilya Chevyrev, Martin Hairer and Lorenzo Zambotti on BPHZ renormalisation of singular SPDEs. In particular, it exploits the graphical representation of expectations of divergent symbols in terms of Feynman diagrams, Zimmermann's forest formula, and the notion of "Hepp sector".
